Multi-Intervention Sequential Decision Modeling
Sequential Decision Model
I built an end-to-end experimental pipeline to improve how reinforcement learning agents make decisions when multiple interventions must be chosen in combination at each timestep. The motivation came from clinical-style decision settings where at each step, a combination of treatments (e.g., drug type, intensity, frequency) must be selected, often with limited data.
Standard reinforcement learning struggles in these environments. As the number of intervention options grows, the action space explodes combinatorially, making learning unstable and sample-inefficient.
We can visualize the intervention options and the state variables as nodes in a graph.
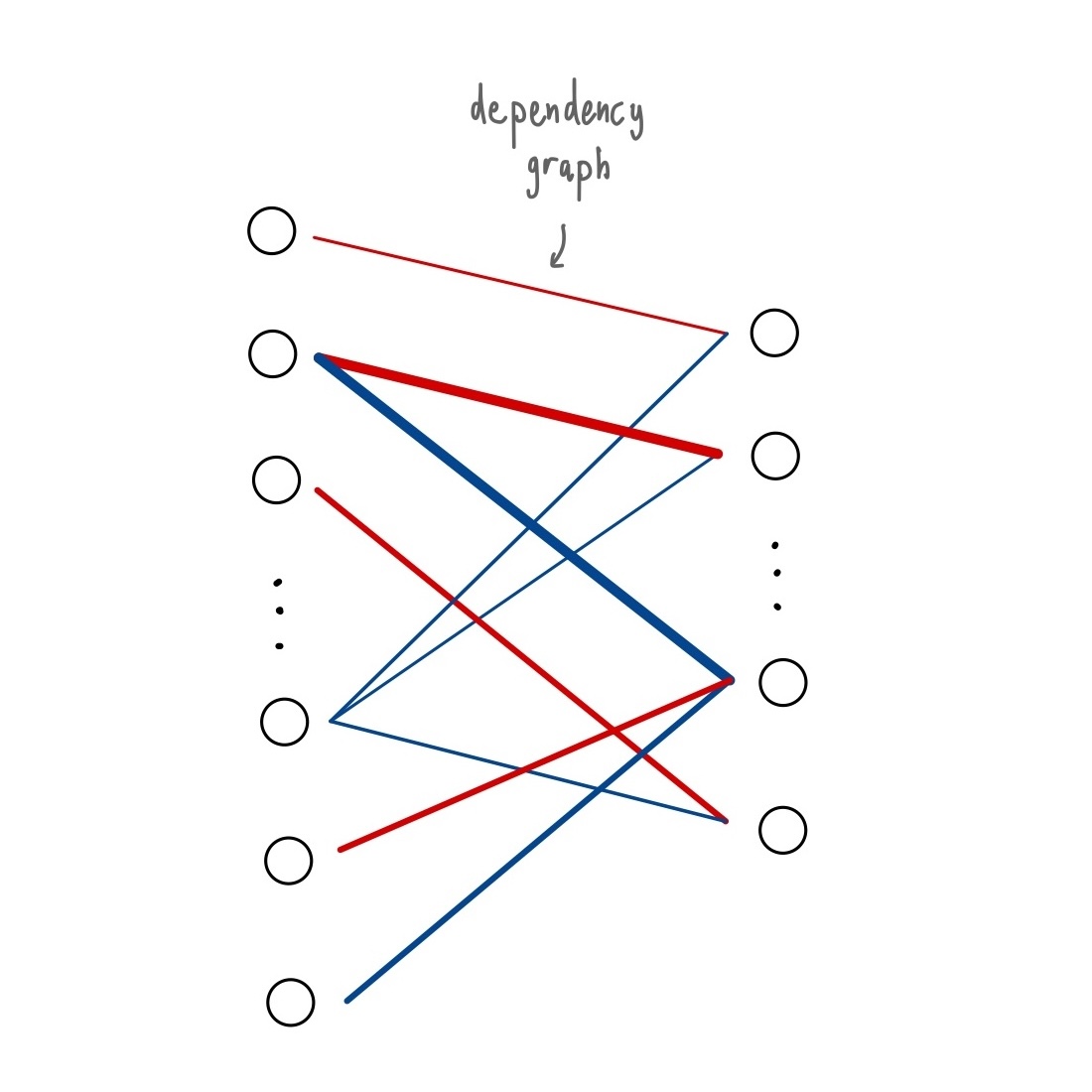
The core idea was to exploit structure. First, we estimate a dependency graph between interventions and system state variables using regression-based methods. This produced an approximate map of how individual interventions influence the system.
We then embed this structure into a graph neural network-based Q-learning architecture. Rather than evaluating every possible intervention combination, the model incrementally constructs an action by estimating the marginal value of individual interventions conditioned on the current state and prior selections.
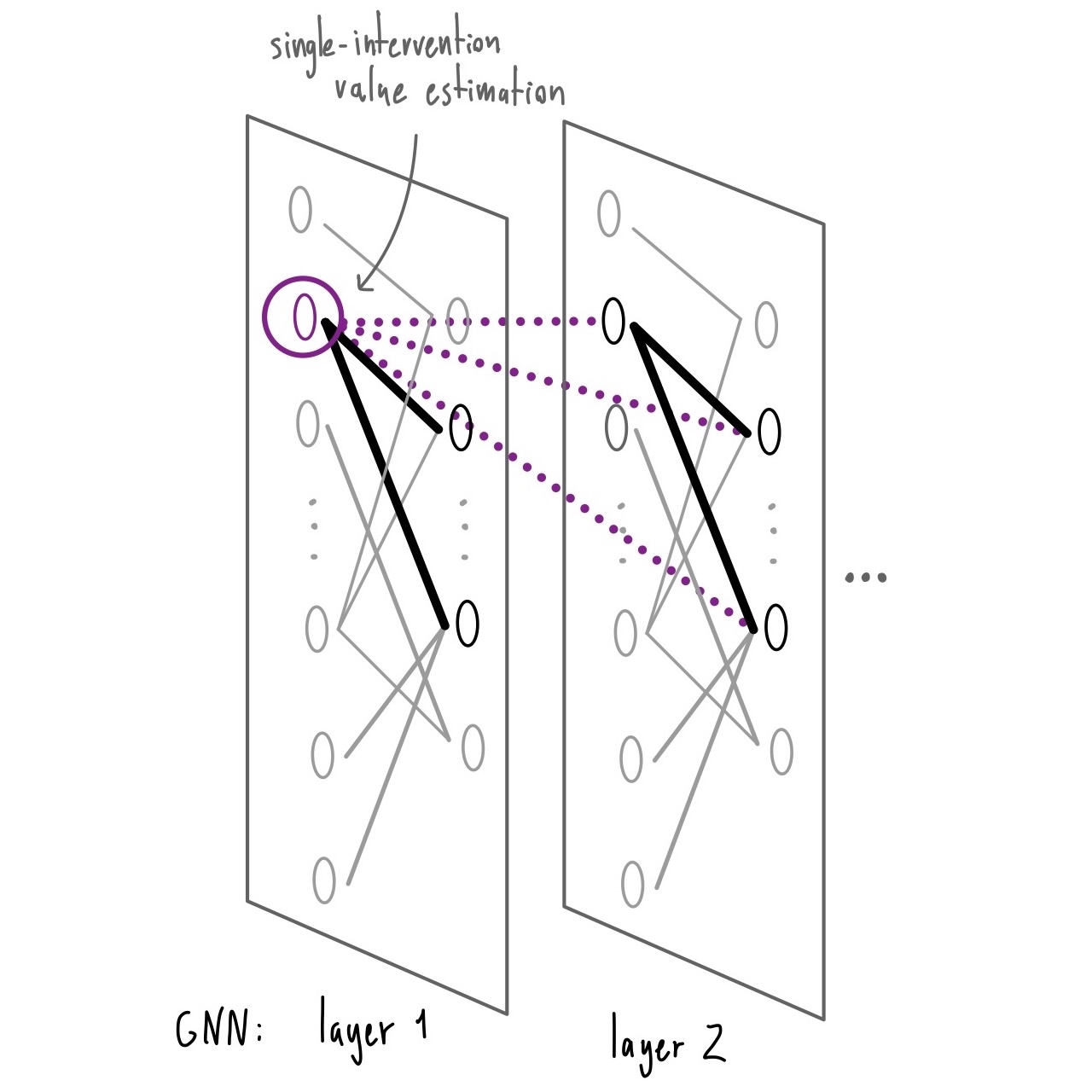
We repeat this process until a choice has been made for all interventions, and this concludes decision making for one timestep.
This reframing avoids exhaustive combination evaluation, and allows each partial decision to incorporate structured information about system dynamics. To support this, I built a full experimental pipeline: synthetic data generation, model training, and controlled experimentation to evaluate performance against the standard approach.
Presentation
Department presentation of this project: